From Pair Programming to Scientific Discovery:
AI as Research Partner
BIO2 Symposium Keynote
August 7, 2025
Talk Overview
Part 1: AI for Biodiversity Research
- Our team’s work
- Connection to bioinformatics and biotechnology
Part 2: The Changing Landscape
- AI agents in software development
- Preparing for the workforce
- Practical integration strategies
AI for Biodiversity ↔︎ Biodiversity for AI
AI → Biodiversity
- Earth faces unprecedented biodiversity crisis
- <10% of ~20M species scientifically named
- Explosion of multimodal data:
- 🧬 DNA barcoding
- 📸 Imaging
- 🎤 Bioacoustics
- Shift from lab to “in-the-wild”
- Foundation models across modalities
Biodiversity → AI
- Complex, hierarchical data structures
- Long-tailed species distribution
- Fine-grained recognition challenges
- Out-of-distribution performance
- Continual learning requirements
Key Statistics
- 5 million specimens
- Images + DNA barcodes + taxonomic labels
- Challenge: Incomplete taxonomic annotations
- Many labels only to family/genus level
- Expert annotation is difficult
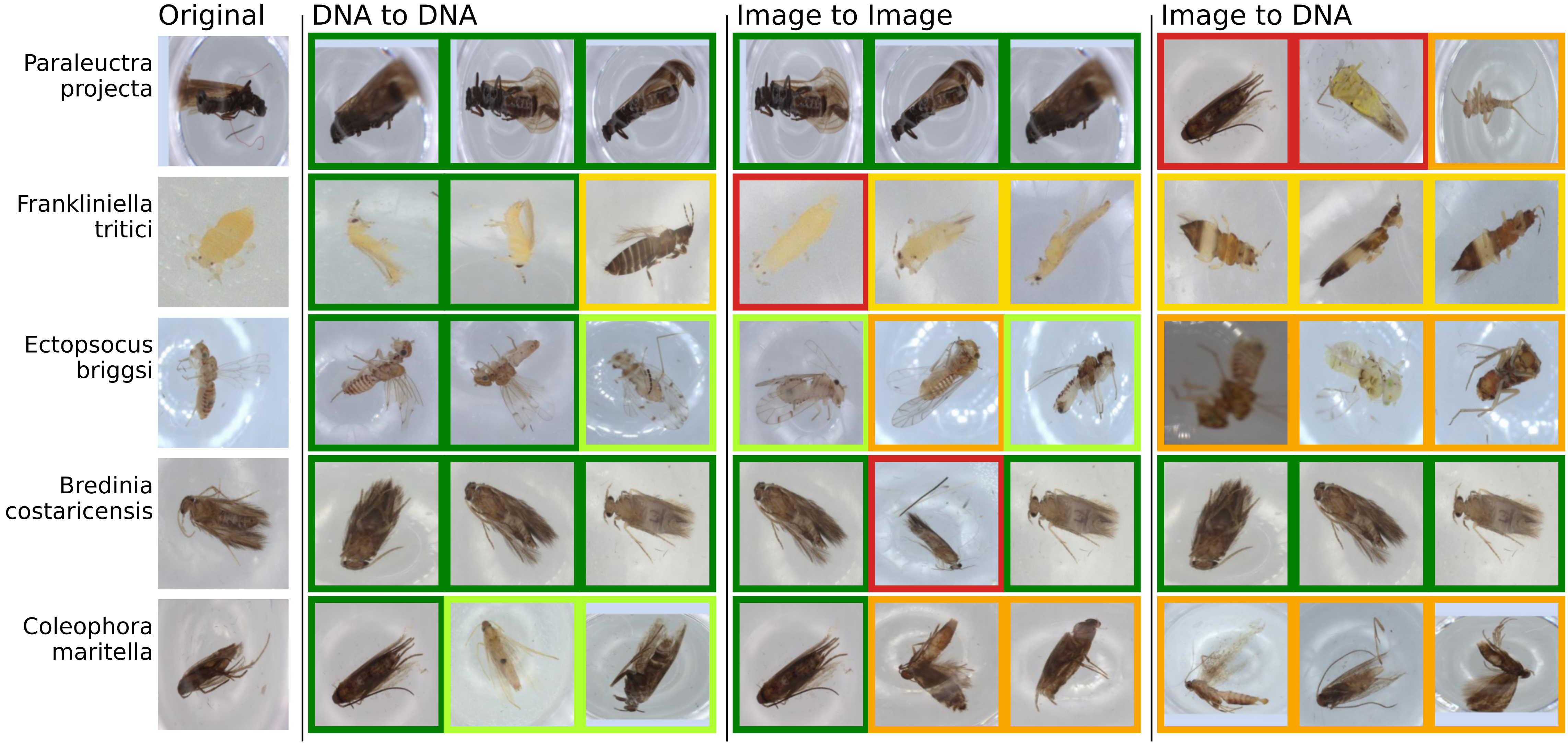
Three-Way Contrastive Learning: CLIBD
Key Innovation
- Three-way contrastive learning
- Vision ↔︎ Text encodings of taxonomic labels ↔︎ DNA
- Cross-modal retrieval
Advantage
Train with DNA, deploy with images only
Image courtesy of Gong et al. 2025
DNA-Supervised Vision: Cost-Effective Deployment

Cost Comparison
- DNA sequencing: $$$
- Image capture: $
Key Insights
- DNA gives fine-grained supervision to vision
- Train expensive, deploy cheap
Image courtesy of Gong et al. 2025
Taxonomic RAG: Beyond Direct Classification
Highlight
- With Nate Lesperance (MBINF alumnus)
Image courtesy of Lesperance et al. 2025
Handling Rare Species Through Retrieval
Note
Traditional (Vision-Only) Approach
- ✓ Great for common species
- ✗ Fails on rare taxa
- ✗ No uncertainty awareness
RAG Approach
- ✓ Handles rare species via text matching
- ✓ Leverages historical text-based records
- ✓ Knows its confidence level
Image courtesy of Lesperance et al. 2025
From Research to Career Questions
“How should I be safely integrating AI into my workflows?”
Why You Shouldn’t Dismiss AI
The pace of change is unprecedented
And it’s accelerating
📈
The METR Study: A New Moore’s Law for AI
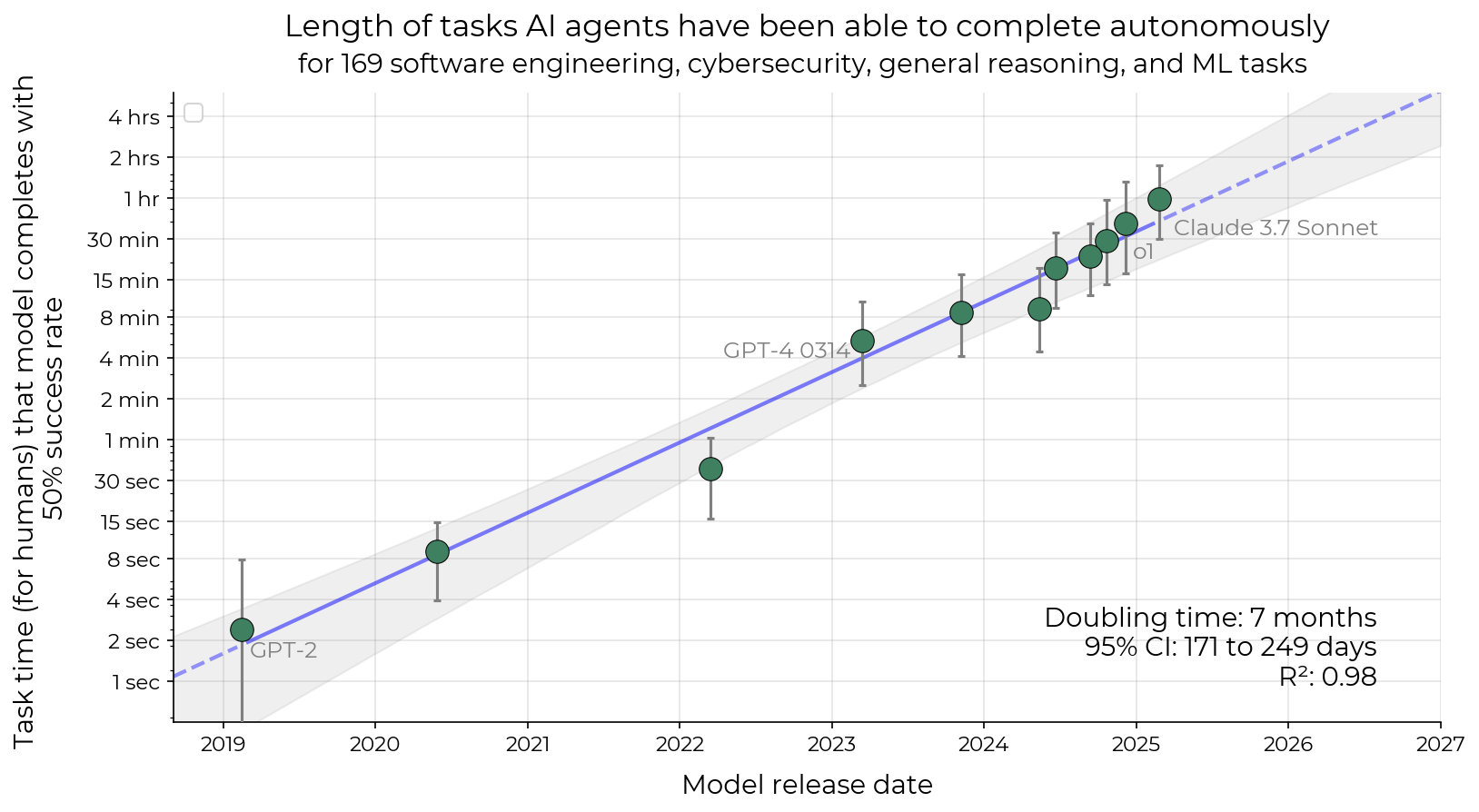
Key Finding
“The length of tasks AI can do is doubling every 7 months” - METR Study
Timeline Evolution
- GPT-4 era: Seconds to minutes of autonomy
- Current models: Minutes to hours of autonomy
- Trend: Exponential capability growth
Image courtesy of METR 2025
Gradual Disempowerment: A Different Kind of Risk
“We might all find ourselves struggling to hold on to money, influence, even relevance. This new world could be more friendly and humane in many ways, while it lasts… But humans would be a drag on growth.”
— David Duvenaud, The Guardian, “Better at everything: how AI could make human beings irrelevant”
The Competitive Reality
Organizations with Humans
- Speed: Slower
- Cost: 2x more expensive
- Reliability: Variable
- Outcome: Outcompeted
Organizations with AI
- Speed: Faster
- Cost: 50% cheaper
- Reliability: Consistent
- Outcome: Market dominance
Organizations that don’t adapt to AI will be displaced by those that do
The Solution: Strategic Integration
Avoiding AI accelerates displacement
Three pillars for thriving in the AI era:
- 🤝 Learn to work WITH AI
- 🧠 Maintain human capabilities
- 🚀 Stay competitive & relevant
Skills Being Automated
🔍 Web Search & Literature Review
- LLM-powered search replacing Google
- Synthesis in seconds vs hours
- Multiple sources browsed automatically
💻 Software Development
- GitHub Copilot, Cursor, Claude Code
- AI agent: 660 commits, top contributor
- From autocomplete to autonomous development
💡 Data Analysis & Ideation
- Creative tasks being automated
- Research ideation affected
- No longer “human-only” territory
Web Search Revolution
“I can feel my usage of Google search taking a nosedive already. I expect a bumpy ride as a new economic model for the Web lurches into view.” - Simon Willison
Two Modes of AI-Powered Search
- Quick Search: 15-30 seconds, 20-40 sources
- Deep Research: 15-30 minutes, comprehensive report


Specialized Research Tools

Elicit - Systematic Reviews
- Extract specific attributes from papers
- High-quality sources only
- Cost: $$$ but streamlined
Other Tools
- Your Agent + Semantic Scholar API
- ResearchRabbit
- Connected Papers
Key Benefit
Quality UI/UX, easy export to other formats
Image courtesy of Elicit
Agentic Coding: The Paradigm Shift
Evolution of AI Coding Tools
- Autocomplete (GitHub Copilot) → seconds of autonomy
- Pair Programming (Cursor) → minutes of autonomy
- Agentic Development (Claude Code) → hours of autonomy
And the result?
“Catnip for programmers”
- Armin Ronacher
Two Approaches: Synchronous vs. Asynchronous
Synchronous (Cursor)
- Work in IDE
- Seconds to minutes
- Pair programming
- Direct oversight
Asynchronous (Claude Code)
- Work via issues/PRs
- Minutes to hours
- Project management
- Multiple agents
Videos courtesy of Simon Willison and Kushagrasikka
The Future: Nerd Managers
Workflow Evolution
- Open GitHub issue
- Agent works autonomously
- Returns with PR
- Review and merge
Future Vision
“Developers will be empowered to keep work queues full in large fleets of coding agents” - Steve Yegge
Video courtesy of All Hands AI
What skills are needed for agentic development?
Graham Neubig from All Hands AI suggests these key skills:
- 🏗️🥧 Strong architecture skills and taste
- 💬 Communication
- 📖 Code reading
- 🔄 Multitasking
Taste and RLHF
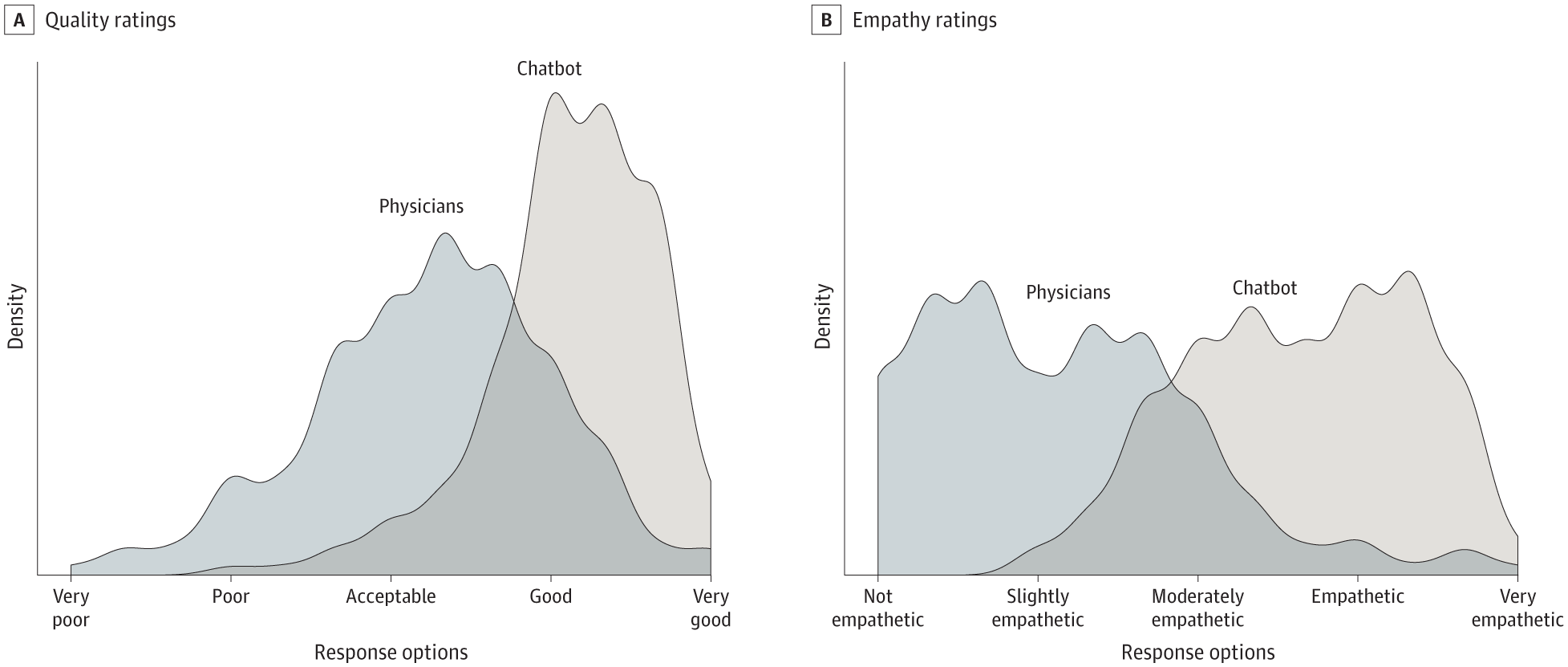
| Imitation (SFT) | RLHF | Why the difference matters |
|---|---|---|
| Model copies full human output distribution. That includes occasional mistakes and mediocre phrasing. Ceiling ≈ human average. | Model samples its own answers and a human simply picks the better one. Humans don’t have to create perfection, only recognise it. | Humans are far stronger critics than creators. Preference-grading lets them steer the model away from the left tail (bad answers) and pull the whole distribution rightward. |
| Training signal = “produce exactly what a human would have written.” | Training signal = “move towards whichever candidate the human preferred.” | Over many iterations the reward model keeps nudging the policy towards the best-judged answers, eventually surpassing the median human. |
Image courtesy of Ayers et al. 2023
Developing Taste in Graduate School
Practice Deliberate Comparison
- Generate multiple AI outputs for the same task and practice choosing which is better, articulating your reasoning
- Develop familiarity with different frontier models and learn what each excels at
- Claude
- ChatGPT
- Gemini
- Platform selection itself is an exercise in taste
Engage in Structured Peer Collaboration
- Seek out reviewing opportunities for conferences and journals to practice evaluating others’ work
- Participate in code review with lab mates or open source projects to develop technical judgment
- Don’t work in isolation - co-author papers with both senior and junior students, getting comfortable with giving and receiving feedback
Seek Active Mentorship
- Ask experienced researchers to walk through their decision-making when they assess quality
- Submit your own quality judgments to mentors for validation and refinement
No “Taste 101” course - learn by doing
The AI Execution Gap
Study details:
- Prior studies found settings where LLM-generated research ideas were judged as more novel than human-expert ideas
- This study: 43 researchers, 100+ hours each
- Randomly assigned to execute AI-generated or human-expert ideas
Image courtesy of Si et al. 2025
Are Junior Developers in Trouble?
MYTH: Junior developers are doomed
REALITY: You’re best positioned to succeed
- ✓ Quick to adopt AI-driven workflows
- ✓ Treat AI tools as on-the-job training
- ✓ Unburdened by legacy tooling
“Junior devs are vibing. They get it. The world is changing, and you have to adapt. So they adapt!”
“It’s not AI’s job to prove it’s better than you. It’s your job to get better using AI.” - Steve Yegge, “Revenge of the Junior Developer”
Two Simple Rules
Rule 1
“AI can be used to avoid learning, and AI can be used to assist learning”
Rule 2
“It’s ok to ask AI to do things you already know how to do,
but don’t ask AI to do things that you don’t know how to do”
Threading the Needle
Finding the right balance between learning with AI and automating with AI

Key Takeaways
Unprecedented change - AI capabilities doubling every 7 months
Avoiding AI accelerates displacement - Engage strategically instead
Develop your taste - The ability to discriminate quality remains crucial
Junior professionals have advantages - Adaptability + experience
Use AI to assist learning, not avoid it - Build skills while automating
Thank You & Resources
Key Papers & Reports
- METR Report (Kwa et al.) on AI Task Completion 📄
- Kulveit and Douglas et al. on “Gradual Disempowerment” 📄
- Si et al. on “The Ideation-Execution Gap” 📄
Practical Resources
- Willison: “AI assisted search-based research actually works now” 📝
- Ronacher: “Agentic Coding” 🎥
- All Hands AI: “What will software dev look like in 2026?” 🎥
- Yegge: “Revenge of the junior developer” 📝
Contact
www.gwtaylor.ca Find me at posters!




